Disclaimer:
APISpec is under active development and not yet production-ready. Feedback, bug reports, and contributions are welcome.
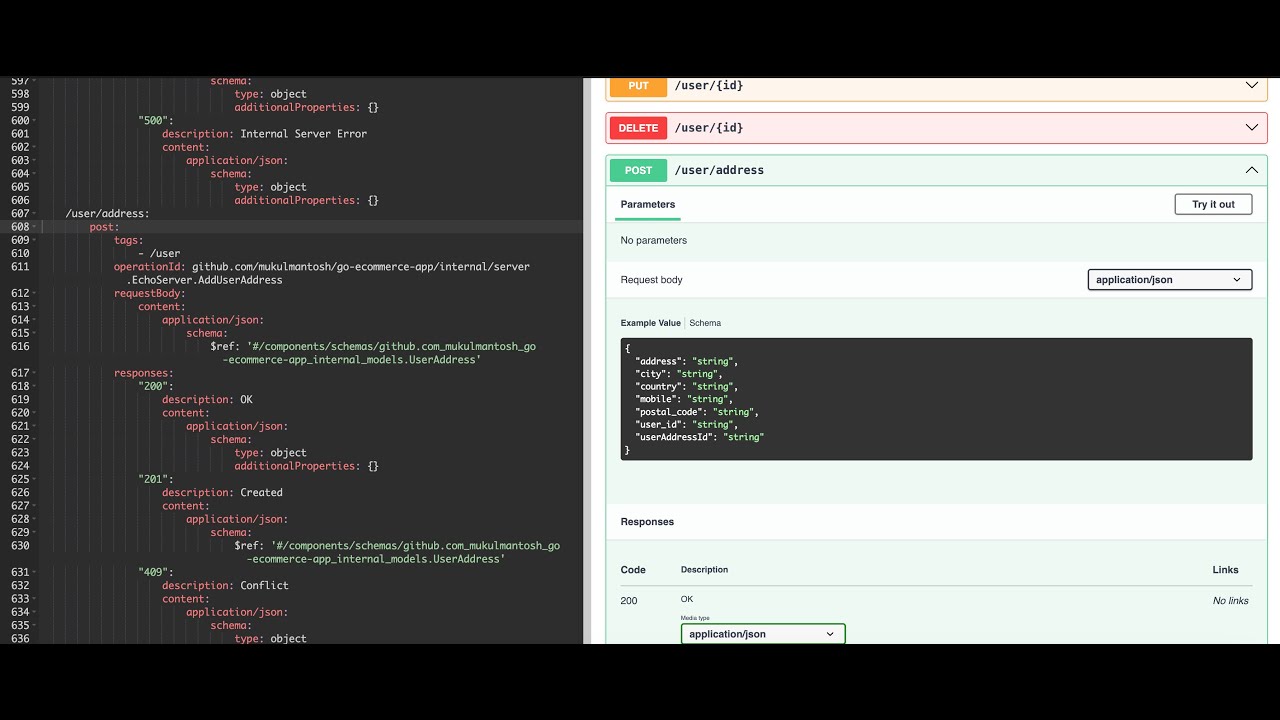
APISpec analyzes your Go code and automatically generates an OpenAPI 3.1 spec (YAML or JSON). It detects routes for popular frameworks (Gin, Echo, Chi, Fiber, net/http), follows call graphs to the final handlers, and infers request/response types from real code (struct tags, literals, generics, and more).
TL;DR: Point APISpec at your module. Get an OpenAPI spec and, optionally, an interactive call-graph diagram.
Click the image above to watch the full demo on YouTube
- Automated OpenAPI: Generate OpenAPI 3.1 from real Go code.
- Framework-aware: Detects Gin, Echo, Chi, Fiber, and net/http automatically.
- Accurate by analysis: Builds a call graph to resolve handlers, parameters, bodies, and responses.
- Configurable: YAML config plus CLI flags; flags always win.
- Visualize: Optional HTML call-graph diagram for debugging.
- Extensible: Pattern-based framework config; add new frameworks without changing core logic.
- Smart Type Resolution: Automatically resolves underlying primitive types for aliases and enums.
- Array Type Support: Comprehensive handling of Go arrays including fixed-size arrays (
[16]byte) and variable-length arrays ([...]int). - External Type Resolution: Automatically resolves external package types to their underlying primitives while preserving internal project types.
- Validator Tag Support: Comprehensive support for go-playground/validator tags with automatic OpenAPI constraint mapping.
- Function Literal Analysis: Full support for anonymous functions in route handlers.
- Comprehensive Error Handling: Robust handling of edge cases and invalid inputs.
- Performance Profiling: Built-in CPU, memory, block, mutex, and trace profiling for performance analysis.
- Configurable Limits: Fine-tune analysis limits for large codebases with detailed warning messages.
- CGO Support: Skip CGO packages during analysis to avoid build errors.
Note: Generating call-graph diagrams and metadata files consumes additional resources and time.
- Route registration: Detects
HandleFuncandHandlecalls with path and handler arguments - Handler function detection: Identifies handler functions passed as arguments to route registration
- HTTP method extraction: Automatically extracts HTTP methods from handler function names or explicit method calls
- Path parameter detection: Recognizes path parameters in route patterns (e.g.,
/users/{id}) - Subrouter support: Handles nested routing with
PathPrefixandSubrouter - Parameter extraction: Path parameters are not yet fully resolved to handler function parameters
- Conditional routing: Dynamic route registration based on runtime conditions is not supported
- Gin: Full support for route registration, and parameter handling
- Chi: Full support for route mounting, grouping, parameter extraction, and render package integration
- Echo: Full support for route registration, grouping, and parameter handling
- Fiber: Full support for route registration, grouping, and parameter handling
- Standard net/http: Basic support for
HandleFuncandHandlecalls
APISpec focuses on practical coverage for real-world services. Current coverage includes:
- Alias imports: supports import aliases in analysis.
- Alias types: type aliases are detected and resolved to underlying primitive types.
- Enum resolution: automatically resolves enum types to their underlying primitive types (string, int, etc.) from constants, enum tags, or oneof validator tags.
- Assignment and alias tracking: short
:=,=, multi-assign, tuple returns, latest-wins resolution, alias chains, and shadowing. - Conditional methods: detecting HTTP methods set via switch/if around net/http
Handle/HandleFuncis not supported. - Composite literals / maps / slices / arrays: recognizes literal and container types for schema mapping.
- Array type support: comprehensive handling of fixed-size arrays (
[16]byte,[5]int) and variable-length arrays ([...]int). - Dependency injection: supports route grouping mounted via dependency injection.
- Duplicate status codes: paths with the same status code and different schemas are not yet supported.
- External type introspection: types from external packages are automatically resolved to their underlying primitives; complex external types can be defined via
externalTypesin config. - Generics (functions): detects type parameters and maps concrete types at call sites.
- Generics (types): generic struct and type instantiation are partially supported.
- Inferred status codes: status codes assigned via variables are not inferred.
- Interfaces: captures interface types and methods; unresolved dynamic values are represented generically.
- Chain calls: efficiently processes method chaining and establishes parent-child relationships in the call graph.
- Nested calls: handles chained/method calls and nested expressions.
- Parameter tracing across calls: follows arguments across the call graph; maps function parameters to call arguments.
- Interface param resolution: interface type parameters in functions are not yet fully resolved to concrete types.
- Parent object type tracing: limited ability to trace the receiver/parent type;
Decodeon non-body targets may be misclassified. - Pointers and dereference: detects
*Tand automatically dereferences when configured. - Selectors and field access: resolves
pkg.Type.Fieldand nested selectors where possible. - Struct fields: reads field types, embedded fields, and struct tags (
json,xml,form, etc.). - Nested struct types: supports anonymous nested structs within struct fields, preserving complete type information for accurate schema generation.
- Function and method return types: automatically resolves and captures return types from function signatures, enabling accurate type resolution in pattern matchers.
- CGO support: includes a flag to skip CGO packages during analysis, useful for projects with complex C dependencies.
- Function literals: supports anonymous functions (func literals) in route handlers and call analysis.
- Validator tag support: comprehensive support for go-playground/validator tags including validation rules, constraints, and enum definitions.
APISpec automatically resolves underlying types for aliases and enums:
// Enum types are resolved to their underlying primitive type
type AllowedUserType string
const (
UserTypeAdmin AllowedUserType = "admin"
UserTypeCustomer AllowedUserType = "user"
)
// In your struct, AllowedUserTypes will be resolved to []string
type Permission struct {
ID string
Resource string
Operation string
AllowedUserTypes []domain.AllowedUserType // Resolves to []string
}
// Generated OpenAPI schema:
// AllowedUserTypes:
// type: array
// items:
// type: string// Pointer aliases are also resolved
type UserID *int64
type User struct {
ID UserID // Resolves to integer
}
// Generated OpenAPI schema:
// ID:
// type: integer
// format: int64APISpec provides comprehensive support for Go arrays, including fixed-size arrays and variable-length arrays:
// Fixed-size byte arrays are converted to string with maxLength
type User struct {
ID [16]byte // Converts to string with format: "byte", maxLength: 16
Token [32]byte // Converts to string with format: "byte", maxLength: 32
Scores [5]int // Converts to array with maxItems: 5, minItems: 5
Tags [10]string // Converts to array with maxItems: 10, minItems: 10
}
// Variable-length arrays
type Config struct {
Values [...]int // Converts to array without size constraints
}User:
type: object
properties:
ID:
type: string
format: byte
maxLength: 16
Token:
type: string
format: byte
maxLength: 32
Scores:
type: array
items:
type: integer
maxItems: 5
minItems: 5
Tags:
type: array
items:
type: string
maxItems: 10
minItems: 10
Config:
type: object
properties:
Values:
type: array
items:
type: integerAPISpec intelligently handles external package types by resolving them to their underlying primitives while preserving internal project types:
// External types (from other packages) are resolved to primitives
import (
"github.com/google/uuid"
"github.com/your-org/shared"
)
type User struct {
ID uuid.UUID // Resolves to string with format: "uuid"
External shared.ExternalType // Resolves to underlying primitive
Internal models.User // Kept as-is (internal project type)
}- External Types: Types from packages like
github.com/google/uuid.UUIDare automatically resolved to their underlying primitive types (e.g.,stringwithformat: "byte") - Internal Types: Types from your own project (even in different packages) are preserved as-is for proper schema generation
- Standard Library: Types like
time.Timeare handled appropriately based on configuration
User:
type: object
properties:
ID:
type: string
format: byte
maxLength: 16
External:
type: string # Resolved from external package
Internal:
$ref: '#/components/schemas/User' # Internal type preservedAPISpec provides comprehensive support for go-playground/validator tags, automatically converting validation rules to OpenAPI schema constraints:
// Status represents different status values
type Status string
// Status constants
const (
StatusActive Status = "active"
StatusInactive Status = "inactive"
StatusPending Status = "pending"
)
type User struct {
ID int `json:"id" validate:"required,min=1"`
Name string `json:"name" validate:"required,min=2,max=50"`
Email string `json:"email" validate:"required,email"`
Age int `json:"age" validate:"min=18,max=120"`
Status Status `json:"status"`
MaritalStatus string `json:"marital_status" validate:"required,oneof=single married divorced"`
Bio string `json:"bio" min:"10" max:"500"`
Website string `json:"website" pattern:"^https?://.*"`
Country string `json:"country" enum:"US,CA,UK,DE,FR"`
}User:
type: object
properties:
age:
type: integer
minimum: 18
maximum: 120
bio:
type: string
country:
type: string
enum:
- US
- CA
- UK
- DE
- FR
email:
type: string
format: email
id:
type: integer
minimum: 1
marital_status:
type: string
enum:
- single
- married
- divorced
name:
type: string
status:
type: string
enum:
- active
- inactive
- pending
website:
type: string
required:
- id
- name
- email
- marital_statusAPISpec supports most go-playground/validator tags:
Note: Some advanced validator tags like
dive(for array element validation) are not yet supported but are planned for future releases.
| Validator Tag | OpenAPI Mapping | Description |
|---|---|---|
required |
required: true |
Field is required |
omitempty |
required: false |
Field is optional |
min=N |
minimum: N |
Minimum value/length |
max=N |
maximum: N |
Maximum value/length |
len=N |
minLength: N, maxLength: N |
Exact length |
email |
format: email |
Email format validation |
url |
format: uri |
URL format validation |
uuid |
format: uuid |
UUID format validation |
oneof=val1 val2 |
enum: [val1, val2] |
Enum values |
alphanum |
pattern: "^[a-zA-Z0-9]+$" |
Alphanumeric characters |
alpha |
pattern: "^[a-zA-Z]+$" |
Alphabetic characters |
numeric |
pattern: "^[0-9]+$" |
Numeric characters |
containsany=chars |
pattern: ".*[chars].*" |
Must contain any of the characters |
e164 |
pattern: "^\\+[1-9]\\d{1,14}$" |
E.164 phone number format |
dive |
❌ Not yet supported | Array element validation |
APISpec now supports anonymous functions in route handlers:
// Gin example with function literals
router.POST("/users", func(c *gin.Context) {
var user CreateUserRequest
if err := c.ShouldBindJSON(&user); err != nil {
c.JSON(400, gin.H{"error": err.Error()})
return
}
// ... handler logic
c.JSON(201, user)
})
// Echo example with function literals
e.POST("/products", func(c echo.Context) error {
var product Product
if err := c.Bind(&product); err != nil {
return c.JSON(400, map[string]string{"error": err.Error()})
}
// ... handler logic
return c.JSON(201, product)
})These function literals are properly analyzed and their request/response types are extracted for OpenAPI generation.
graph TD
A[Go Source Code] --> B[Package Analysis & Type Checking]
B --> C[Framework Detection]
C --> D[Metadata Generation]
D --> E[Call Graph Construction]
E --> F[Tracker Tree with Limits]
G[Config File<br/>--config] -.-> H[Pattern Extraction]
F --> H
D --> H
H --> I[OpenAPI Spec Generation]
I --> J{{Output Format?}}
J -->|JSON| K[openapi.json]
J -->|YAML| L[openapi.yaml]
E -.-> M[Call Graph Diagram<br/>--diagram]
M -.-> N[diagram.html]
H -.-> O[Effective Config Output<br/>--output-config]
O -.-> P[apispec-config.yaml]
D -.-> Q[Metadata Output<br/>--write-metadata]
Q -.-> R[metadata.yaml]
APISpec executes a multi-stage process to analyze your code and generate the OpenAPI specification. The workflow is designed to be robust and flexible, handling complex Go projects with ease.
-
Initialization & Flag Parsing: The tool starts, prints license information, and parses all command-line flags provided by the user.
-
Module Discovery: It finds the root of the Go module by searching for the
go.modfile and changes the working directory to the module root. -
Package Loading & Type-Checking: APISpec loads and performs a full type-check on all Go packages within the module (
./...), building a rich understanding of the code's types and syntax. -
Framework Detection: It analyzes the project's dependencies to automatically detect the web framework being used (e.g., Gin, Chi, Echo, Fiber, or standard
net/http). -
Configuration Loading: The tool loads a framework-specific default configuration. If a custom
--configfile is provided, it loads that instead. CLI flags always override settings from any configuration file. -
Metadata Generation: It traverses the Abstract Syntax Trees (AST) of the parsed packages to generate a detailed
metadataobject. This object contains information about packages, function calls, and string constants. -
Call Graph Construction: Using the generated metadata, APISpec constructs a call graph tree. This tree traces the flow of execution from router definitions to the final handler functions, respecting limits set by flags like
--max-nodesto prevent infinite recursion. -
OpenAPI Mapping: The call graph and metadata are processed by a framework-specific mapper. This mapper identifies API routes, parameters, request bodies, and responses, translating them into the OpenAPI specification structure.
-
Specification Generation: The final OpenAPI object is marshaled into either YAML or JSON format, based on the output file extension (
.yaml, or.json). -
File Output: The resulting specification file is written to the path specified by the
--outputflag. If requested, an interactive HTML call graph diagram is also generated.
📖 For detailed installation instructions, see INSTALLATION.md
go install github.com/ehabterra/apispec/cmd/apispec@latest# Clone the repository
git clone https://github.com/ehabterra/apispec.git
cd apispec
# Build and install
make install-local # Install to ~/go/bin (no sudo required)
# OR
make install # Install to /usr/local/bin (requires sudo)# Download and run the installation script
curl -sSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ehabterra/apispec/main/scripts/install.sh | bash -s go-installNote: Make sure your Go bin directory is in your PATH. Add this to your shell profile:
export PATH=$HOME/go/bin:$PATH# Clone the repository
git clone https://github.com/ehabterra/apispec.git
cd apispec
# Build the binary
make build
# Or build directly with Go
go build -o apispec ./cmd/apispec
# Build the API diagram server
go build -o apidiag ./cmd/apidiag# Generate OpenAPI spec from your Go project
./apispec --output openapi.yaml
# Generate with custom config
./apispec --config my-config.yaml --output openapi.yaml
# Generate with call graph diagram
./apispec --output openapi.yaml --diagram diagram.html
# Generate metadata for debugging
./apispec --output openapi.yaml --write-metadata
# Performance profiling for large codebases
./apispec --output openapi.yaml --cpu-profile --mem-profile
# Skip CGO packages to avoid build errors
./apispec --output openapi.yaml --skip-cgo
# Fine-tune analysis limits for large projects
./apispec --output openapi.yaml --max-nodes 100000 --max-children 1000 --max-recursion-depth 15APISpec includes a web-based API diagram server (apidiag) that provides an interactive interface for exploring call graphs. This is particularly useful for large codebases where static diagrams become unwieldy.
# Start the API diagram server
./apidiag
# Or if installed globally
apidiag
# Open your browser to http://localhost:8080- Interactive Web Interface: Browse call graphs through a modern web UI
- Paginated Visualization: Handle large codebases with efficient pagination
- Advanced Filtering: Filter by packages, functions, files, receivers, signatures, and more
- Real-time Analysis: Live analysis of your Go project structure
- Export Capabilities: Export diagrams in multiple formats (SVG, PNG, PDF, JSON)
- RESTful API: Programmatic access to diagram data
# Start server on custom port
./apidiag --port 9090
# Analyze specific directory
./apidiag --dir ./my-go-project
# Custom page size and depth
./apidiag --page-size 50 --max-depth 2
# Show version information
./apidiag --version📖 For detailed documentation, see cmd/apidiag/README.md
import (
"os"
"github.com/ehabterra/apispec/generator"
"github.com/ehabterra/apispec/spec"
"gopkg.in/yaml.v3"
)
func main() {
cfg := spec.DefaultGinConfig() // or spec.LoadAPISpecConfig("apispec.yaml")
gen := generator.NewGenerator(cfg)
openapi, err := gen.GenerateFromDirectory("./your-project")
if err != nil { panic(err) }
data, _ := yaml.Marshal(openapi)
os.WriteFile("openapi.yaml", data, 0644)
}| Full Flag | Shorthand | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
--output |
-o |
Output file for OpenAPI spec | openapi.json |
--dir |
-d |
Directory to parse for Go files | . (current dir) |
--title |
-t |
Title of the API | Generated API |
--api-version |
-v |
Version of the API | 1.0.0 |
--description |
-D |
API description | "" |
--terms-url |
-T |
Terms of Service URL | "" |
--contact-name |
-N |
Contact person/organization name | Ehab |
--contact-url |
-U |
Contact URL | https://ehabterra.github.io/ |
--contact-email |
-E |
Contact email | [email protected] |
--license-name |
-L |
License name | "" |
--license-url |
-lu |
License URL | "" |
--openapi-version |
-O |
OpenAPI spec version | 3.1.1 |
--config |
-c |
Path to custom config YAML | "" |
--output-config |
-oc |
Output effective config to YAML | "" |
--write-metadata |
-w |
Write metadata.yaml to disk | false |
--split-metadata |
-s |
Split metadata into separate files | false |
--diagram |
-g |
Save call graph as HTML | "" |
--max-nodes |
-mn |
Max nodes in call graph tree | 50000 |
--max-children |
-mc |
Max children per node | 500 |
--max-args |
-ma |
Max arguments per function | 100 |
--max-depth |
-md |
Max depth for nested arguments | 100 |
--max-recursion-depth |
-mrd |
Max recursion depth to prevent infinite loops | 10 |
--skip-cgo |
Skip CGO packages during analysis | true |
|
--include-file |
Include files matching pattern (multiple) | "" |
|
--include-package |
Include packages matching pattern (multiple) | "" |
|
--include-function |
Include functions matching pattern (multiple) | "" |
|
--include-type |
Include types matching pattern (multiple) | "" |
|
--exclude-file |
Exclude files matching pattern (multiple) | "" |
|
--exclude-package |
Exclude packages matching pattern (multiple) | "" |
|
--exclude-function |
Exclude functions matching pattern (multiple) | "" |
|
--exclude-type |
Exclude types matching pattern (multiple) | "" |
|
--cpu-profile |
Enable CPU profiling | false |
|
--mem-profile |
Enable memory profiling | false |
|
--block-profile |
Enable block profiling | false |
|
--mutex-profile |
Enable mutex profiling | false |
|
--trace-profile |
Enable trace profiling | false |
|
--custom-metrics |
Enable custom metrics collection | false |
|
--profile-dir |
Directory for profiling output files | profiles |
openapi: 3.1.0
info:
title: User Management API
version: 1.0.0
description: API for managing users and permissions
paths:
/users:
get:
summary: List users
parameters:
- name: page
in: query
schema:
type: integer
minimum: 1
default: 1
- name: limit
in: query
schema:
type: integer
minimum: 1
maximum: 100
default: 20
responses:
'200':
description: List of users
content:
application/json:
schema:
type: object
properties:
users:
type: array
items:
$ref: '#/components/schemas/User'
pagination:
$ref: '#/components/schemas/Pagination'
post:
summary: Create user
requestBody:
required: true
content:
application/json:
schema:
$ref: '#/components/schemas/CreateUserRequest'
responses:
'201':
description: User created successfully
content:
application/json:
schema:
$ref: '#/components/schemas/User'
'400':
description: Invalid request data
/users/{id}:
get:
summary: Get user by ID
parameters:
- name: id
in: path
required: true
schema:
type: string
format: uuid
responses:
'200':
description: User details
content:
application/json:
schema:
$ref: '#/components/schemas/User'
'404':
description: User not found
components:
schemas:
User:
type: object
properties:
id:
type: string
format: uuid
name:
type: string
email:
type: string
format: email
status:
type: string
enum: ["active", "inactive", "pending"]
createdAt:
type: string
format: date-time
permissions:
type: array
items:
type: string
enum: ["admin", "user", "driver", "store_manager", "picker"]
required: ["id", "name", "email"]
CreateUserRequest:
type: object
properties:
name:
type: string
email:
type: string
format: email
permissions:
type: array
items:
type: string
required: ["name", "email"]
Pagination:
type: object
properties:
page:
type: integer
minimum: 1
limit:
type: integer
minimum: 1
total:
type: integer
totalPages:
type: integerAPISpec uses YAML configuration files to define framework patterns and behavior. Here are examples for different frameworks:
# Example Gin configuration (apispec.yaml)
info:
title: My API
version: 1.0.0
description: A comprehensive API for user management
framework:
routePatterns:
- callRegex: ^(?i)(GET|POST|PUT|DELETE|PATCH|OPTIONS|HEAD)$
recvTypeRegex: ^github\.com/gin-gonic/gin\.\*(Engine|RouterGroup)$
handlerArgIndex: 1
methodFromCall: true
pathFromArg: true
handlerFromArg: true
requestBodyPatterns:
- callRegex: ^(?i)(BindJSON|ShouldBindJSON|BindXML|BindYAML|BindForm|ShouldBind)$
typeFromArg: true
deref: true
- callRegex: ^Decode$
typeFromArg: true
deref: true
- callRegex: ^Unmarshal$
typeArgIndex: 1
typeFromArg: true
deref: true
responsePatterns:
- callRegex: ^(?i)(JSON|String|XML|YAML|ProtoBuf|Data|File|Redirect)$
typeArgIndex: 1
statusFromArg: true
typeFromArg: true
- callRegex: ^Marshal$
typeFromArg: true
deref: true
- callRegex: ^Encode$
typeFromArg: true
deref: true
paramPatterns:
- callRegex: ^Param$
paramIn: path
- callRegex: ^Query$
paramIn: query
- callRegex: ^DefaultQuery$
paramIn: query
- callRegex: ^GetHeader$
paramIn: header
mountPatterns:
- callRegex: ^Group$
recvTypeRegex: ^github\.com/gin-gonic/gin\.\*(Engine|RouterGroup)$
routerArgIndex: 1
pathFromArg: true
routerFromArg: true
isMount: true
# Type mappings for custom types and external packages
typeMapping:
- goType: time.Time
openapiType:
type: string
format: date-time
- goType: uuid.UUID
openapiType:
type: string
format: uuid
- goType: decimal.Decimal
openapiType:
type: string
format: decimal
# Validator tag support is automatically enabled
# APISpec will parse validate tags and convert them to OpenAPI constraints
# Example: validate:"required,email" -> required: true, format: email
# External types that can't be introspected automatically
# Note: APISpec automatically resolves external package types to their underlying primitives
# Only define complex external types that need custom schemas here
externalTypes:
- name: github.com/gin-gonic/gin.H
openapiType:
type: object
additionalProperties: true
- name: github.com/your-package/CustomResponse
openapiType:
type: object
properties:
success:
type: boolean
data:
type: object
message:
type: string# Example Echo configuration
framework:
routePatterns:
- callRegex: ^(?i)(GET|POST|PUT|DELETE|PATCH|OPTIONS|HEAD)$
recvTypeRegex: ^github\.com/labstack/echo\.\*(Echo|Group)$
handlerArgIndex: 1
methodFromCall: true
pathFromArg: true
handlerFromArg: true
requestBodyPatterns:
- callRegex: ^(?i)(Bind|BindJSON|BindXML|BindYAML)$
typeFromArg: true
deref: true
responsePatterns:
- callRegex: ^(?i)(JSON|String|XML|YAML|Blob|File|Stream)$
typeArgIndex: 1
statusFromArg: true
typeFromArg: true
paramPatterns:
- callRegex: ^Param$
paramIn: path
- callRegex: ^QueryParam$
paramIn: query
- callRegex: ^FormValue$
paramIn: formData# Handle custom domain types
typeMapping:
- goType: domain.UserStatus
openapiType:
type: string
enum: ["active", "inactive", "pending"]
- goType: domain.Priority
openapiType:
type: integer
enum: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
- goType: []domain.Tag
openapiType:
type: array
items:
type: string# Define schemas for external packages
externalTypes:
- name: github.com/your-org/shared.Response
openapiType:
type: object
properties:
code:
type: integer
message:
type: string
data:
type: object
additionalProperties: true
- name: github.com/your-org/shared.Pagination
openapiType:
type: object
properties:
page:
type: integer
minimum: 1
limit:
type: integer
minimum: 1
maximum: 100
total:
type: integer- Go 1.24+ (Didn't test it on version before 1.24)
- Understanding of AST (Abstract Syntax Tree)
- Familiarity with OpenAPI 3.1 specification
apispec/
├── cmd/
│ └── apispec/ # CLI entry point
│ └── main.go
├── generator/ # High-level generator interface
│ ├── generator.go
│ └── generator_test.go
├── internal/
│ ├── core/ # Framework detection and core logic
│ ├── engine/ # Processing engine
│ ├── metadata/ # Code analysis and metadata extraction
│ └── spec/ # OpenAPI spec generation and mapping
├── spec/ # Public spec package
├── testdata/ # Example projects for testing
├── scripts/ # Build and utility scripts
├── docs/ # Documentation files
└── .github/ # GitHub workflows and templates
# Run all tests
make test
# Run tests with coverage
make coverage
# Run comprehensive mapper tests
go test ./internal/spec -v -run "Test.*Comprehensive"
# Build the binary
make build
# Update coverage badge
make update-badgeAPISpec includes comprehensive test suites covering:
- Unit tests for all packages
- Integration tests for framework detection and OpenAPI generation
- Comprehensive mapper tests for edge cases and type resolution
- Framework-specific tests for Gin, Echo, Chi, and Fiber
Run specific test categories:
# Test mapper functionality
go test ./internal/spec -v
# Test metadata extraction
go test ./internal/metadata -v
# Test with coverage
go test ./... -cover- Fork the repository
- Create a feature branch (
git checkout -b feature/amazing-feature) - Add tests for new functionality
- Run tests to ensure everything works (
make test) - Update coverage badge (
make update-badge) - Commit your changes (
git commit -m 'Add amazing feature') - Push to the branch (
git push origin feature/amazing-feature) - Open a Pull Request
- Update the framework detection logic in
internal/core/detector.go - Add default configuration in
internal/spec/config.go - Update the framework detection logic in
cmd/apispec/main.go - Add test cases in
testdata/
- All code should have tests
- Aim to maintain or improve test coverage
- Follow Go coding standards
- Add documentation for new features
APISpec includes built-in profiling capabilities to help you analyze and optimize performance:
- CPU Profiling: Analyze function execution time and call frequency
- Memory Profiling: Track memory allocation patterns and identify leaks
- Block Profiling: Detect goroutine blocking issues
- Mutex Profiling: Identify mutex contention problems
- Trace Profiling: Detailed execution trace analysis
- Custom Metrics: Application-specific performance metrics
# Basic CPU profiling
./apispec -d ./my-project --cpu-profile
# Comprehensive profiling
./apispec -d ./my-project --cpu-profile --mem-profile --custom-metrics
# Custom profiling directory
./apispec -d ./my-project --cpu-profile --profile-dir ./analysis
# Analyze with Go tools
go tool pprof profiles/cpu.prof
go tool pprof profiles/mem.prof
go tool trace profiles/trace.outThe custom metrics collector automatically tracks:
- Memory usage patterns
- Goroutine counts
- Function execution times
- System resource utilization
Generated metrics are saved as JSON and can be analyzed for performance insights.
APISpec implements several safeguards to prevent excessive resource usage:
| Parameter | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| MaxNodesPerTree | 50,000 | Maximum nodes in call graph |
| MaxChildrenPerNode | 500 | Children per node |
| MaxArgsPerFunction | 100 | Arguments per function |
| MaxNestedArgsDepth | 100 | Argument nesting depth |
| MaxRecursionDepth | 10 | Maximum recursion depth to prevent infinite loops |
Warning Messages: APISpec now provides clear warnings when limits are reached:
Warning: MaxNodesPerTree limit (50000) reached, truncating tree at node example.com/pkg.Function
Warning: MaxChildrenPerNode limit (500) reached for node example.com/pkg.Function, truncating children
Warning: MaxRecursionDepth limit (10) reached for node example.com/pkg.FunctionAdjust these with CLI flags if needed for large codebases.
- docs/INSTALLATION.md: Detailed installation instructions
- docs/RELEASE_WORKFLOW.md: Automated release process with GitHub Actions
- docs/TRACKER_TREE_USAGE.md: Guide to using TrackerTree for call graph analysis
- docs/CYTOGRAPHE_README.md: Documentation for the call graph visualization feature
- cmd/apispec/README.md: Main CLI tool documentation
- cmd/apidiag/README.md: Interactive API diagram server documentation
- internal/metadata/README.md: Metadata package documentation
- internal/spec/README.md: Spec generation package documentation
Apache License 2.0 - See LICENSE for details.